Brain Hemispheres
The brain is divided in half, through the middle and we call these hemispheres.

The Left Hemisphere (Blue)
This half is responsible for:
- Logical reasoning
- Analytical thinking
- Language processing
- Controls the right side of the body
The Right Hemisphere (Purple)
This half is responsible for :
- Creativity
- Spatial ability
- Artistic skills
- Controls the left side of the body
The Lobes
The brain is divided into 4 lobes. Each lobe is responsible for seperate processes.

The Frontal Lobe (Blue)
The frontal lobe is key for decision making, problem-solving, emotions, and voluntary movement. Issues in this area can lead to problems with anger management.
The Parietal Lobe (Yellow)
This lobe processes sensory information, spatial sense, and navigation.
The Occipital Lobe (Red)
The occipital lobe is primarily responsible for vision processing.
The Temporal Lobe (Green)
The temporal lobe handles auditory processing, speech semantics, and memory formation.
Cerebrum
The cerebrum is responsible for various high-level brain functions, including thought and action.
Cerebral Cortex
One of the key parts of the cerebrum is the Cerebral Cortex, the brain's outer layer, which plays a vital role in consciousness, thought, emotion, reasoning, language, and memory. It is divided into six regions, each responsible for different functions:
Frontal Cortex

The frontal cortex is a part of the frontal lobe, specifically referring to the outer layer involved in higher-level cognitive functions like decision-making, planning, and emotion regulation.
Motor Cortex

The motor cortex is responsible for controlling voluntary movements by sending signals to muscles.
Somatosensory Cortex

This cortex processes sensory input from the body, allowing us to perceive touch, pressure, temperature, and pain.
Visual Cortex

Located in the occipital lobe, it processes visual information from the eyes, enabling us to interpret and respond to what we see.
Auditory Cortex

Found in the temporal lobe, it processes auditory information, essential for hearing and understanding sounds.
Cerebellum

The cerebellum is a crucial part of the brain responsible for coordinating muscle movements, maintaining posture, and ensuring balance. It processes information from the sensory systems, spinal cord, and other parts of the brain to provide precise timing and appropriate patterns of skeletal muscle contraction, thus enabling smooth, coordinated movements and proper body posture.
The Brainstem

The brainstem controls several vital functions necessary for survival and acts as a relay center connecting the cerebrum and cerebellum to the spinal cord. It is further divided into 3 main parts:
Midbrain

The midbrain is involved in functions such as vision, hearing, eye movement, and body movement. It helps process visual and auditory information and is essential for reflexes associated with these senses.
Pons

The pons connects the upper and lower parts of the brain, playing a crucial role in breathing and facilitating communication between different parts of the brain. It also assists in regulating sleep cycles.
Medulla Oblongata

The medulla oblongata controls autonomic functions such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure. It is vital for maintaining basic life functions and ensuring survival.
The Limbic System
The limbic system is crucial for emotion regulation, memory, and arousal. It consists of six interconnected structures that support emotional and motivational behaviours.
Amygdala

The amygdala is involved in regulating emotions and memory, particularly those related to fear and pleasure. Overactivity in this area can lead to anxiety disorders.
Hippocampus

The hippocampus is essential for memory formation and spatial navigation. Damage to this area can cause memory problems and difficulty forming new memories.
Thalamus

The thalamus acts as the brain’s relay station, directing sensory and motor signals to the cerebral cortex. It plays a critical role in processing and transmitting information.
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus regulates vital functions such as temperature, hunger, thirst, and circadian rhythms. It helps maintain the body’s internal balance.
Cingulate Gyrus
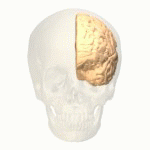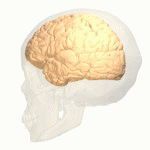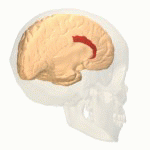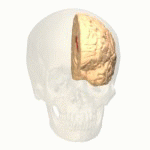
The cingulate gyrus is involved in processing emotions and regulating behavior. It helps link behavioral outcomes to motivation and emotional responses.
Basal Ganglia
The basal ganglia are involved in movement regulation and reward processing. They play a role in motor control and learning from rewards and punishments.
Autonomic Nervous System
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates involuntary body functions, such as :
- Heart rate
- Digestion
- Respiratory rate
- Blood pressure
It operates automatically without conscious direction and is divided into two main branches:.
- The sympathetic nervous system
- The parasympathetic nervous system
Sympathetic Nervous System
The sympathetic nervous system prepares the body for 'fight or flight' response during stressful situations. It increases heart rate, dilates pupils, and redirects blood flow to muscles, preparing the body to face or flee from threats. Prolonged activation can lead to chronic stress and anxiety disorders.
- The hypothalamus plays a key role in activating the sympathetic nervous system by triggering the release of stress hormones.
- The medulla oblongata in the brainstem is involved in controlling autonomic functions such as heart rate and blood pressure during sympathetic activation.
Parasympathetic Nervous System
The parasympathetic nervous system promotes the 'rest and digest' response. It helps conserve energy by slowing the heart rate, increasing intestinal and gland activity, and relaxing sphincter muscles in the gastrointestinal tract. This system is essential for recovery and maintaining homeostasis after stress.
- The vagus nerve is a major component of the parasympathetic nervous system, influencing heart rate, digestion, and other functions.
- The brainstem, particularly the medulla oblongata, plays a crucial role in regulating parasympathetic activities such as lowering blood pressure and heart rate.
What Are Neurotransmitters?
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers in the brain that play a crucial role in transmitting signals between neurons.
Dopamine
Dopamine is involved in reward and motivation. Imbalances in dopamine levels can lead to conditions such as schiznophrenia.
Serotonin
Serotonin regulates mood, appetite, and sleep. Low levels of serotonin are commonly linked to depression.
Acetylcholine
Acetylcholine is important for muscle action, learning, and memory. It facilitates communication between neurons and muscles.
GABA (Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid)
GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter that reduces neuronal excitability, helping to regulate nervous system activity and prevent over-excitation.
